UNIX环境高级编程学习之第七章进程环境-环境变量表读取/添加/修改/删除 [code lang="cpp"]#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char* pValue; pValue = getenv("HOME"); // 起始目录(主目录) // printf("$HOME = %s/n", pValue); // 在主目录下…
UNIX环境高级编程学习之第七章进程环境-存储器分配malloc [code lang="cpp"]#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> char* newChar(int size) { return (char*)malloc(size); } int newInt(int** ppInt…
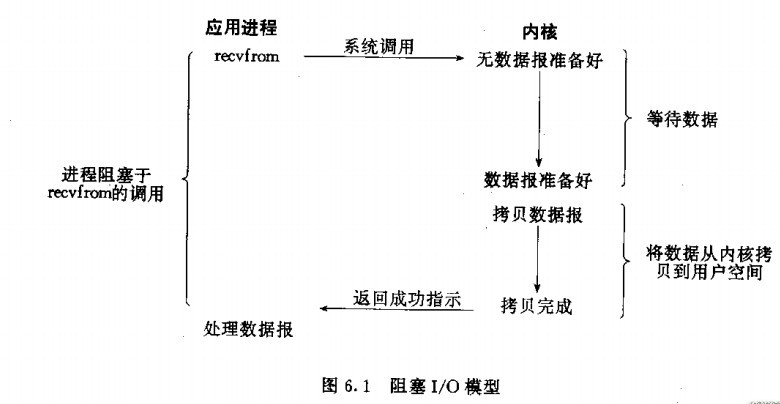
socket阻塞与非阻塞,同步与异步 作者:huangguisu 1. 概念理解 在进行网络编程时,我们常常见到同步(Sync)/异步(Async),阻塞(Block)/非阻塞(Unblock)四种调用方式: 同步: 所谓同步,就是在发出一个功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用就不返回。也就是必须一件一件事做,等前一件做完了才能做下一件事。 例如普通B/S模式(同步):提交请求->等待服务器处理->处理完毕返回 这个期间客户端浏览器不能干任何事 异步: 异步的概念和同步相对。当一个异步过程调用发出后,…
UNIX环境高级编程学习之第六章系统数据文件和信息 用链表的形式读出一个服务器的远程用户登入登出信息 [code lang="cpp"]#pragma pack(1) #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcn…
UNIX环境高级编程学习之第六章系统数据文件和信息-修改第四章实现的Shell的“ls -l”功能, 加入显示文件的用户名和组名 [code lang="cpp"]// 只能查看目录中的所有文件属性 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <dirent.h> …
UNIX环境高级编程学习之第六章系统数据文件和信息-GID To GroupName [code lang="cpp"] #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <grp.h> char * gidToGroupName(char *szGroupName, gid_t gid) { struct group* gtr; gtr = getgrgid(gid); strcp…